The terms UX and UI design are now common in our daily lives. You’ve probably heard these acronyms, mostly used in product design and web development. UI vs UX design is a long debate that concludes that a digital product requires both designs to make a successful and easy-to-use product. A superb product experience begins with UX, which is followed by UI. The efficiency of the product depends on both. But what is the difference between these two? We will discuss that in our article below.
What is UX design?
The term “user experience” (UX) describes how a user interacts with a product or service. It places a strong emphasis on the product’s usability, effectiveness, experience, and feelings that users get from using it. Thus, the primary goal of UX designers is to guarantee clients find a product that is productive, fun, and easy to use.
What is UI design?
All of the interactive and visual components of digital products are represented by user interface design, or UI design. This refers to everything that people can view, click on, or use on a screen. In addition to being aesthetically pleasing and visually appealing, a good user interface (UI) guarantees easy user navigation. The arrangement of buttons, color schemes, and typefaces are the key elements of an interface that go a long way toward making a product that is easy to use and leaves users feeling satisfied.
Read Our Article
UI vs UX Design Job Responsibilities
The duties and responsibilities of a UI designer consist of:
- Establishing the product’s visual identity.
- Setting the color scheme and typography.
- Drafting guidelines for style.
- Adding interactive and visual components to layouts
- Establishing and improving the system of design
- Creating wireframes and mockup designs
The duties and responsibilities of a UX designer consist of:
- Putting a system of information to use
- Carrying out user research
- Developing wireframes, prototypes, and the first layout
- Storyboarding and establishing user profiles
- Developing and assessing user flows, journeys, and personas
- Examining data in regard to the results
UI vs UX Design Key Differences
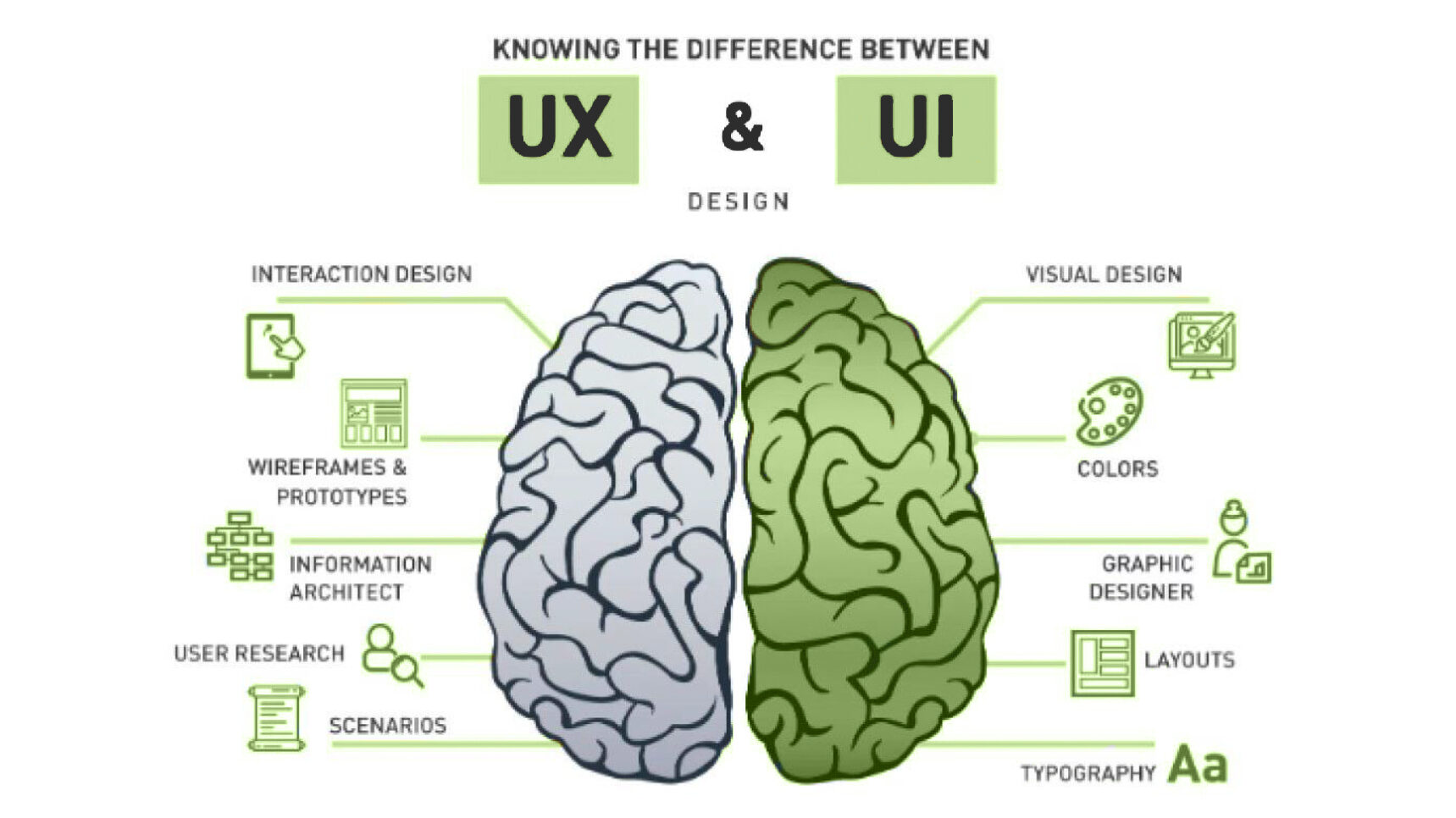
UX and UI assist each other, yet each has its own purpose. They’re frequently compared to architects. Similar to an architect, a UX designer is concerned with the building’s entire structure, it’s functioning, and its practical layout. Similar to interior designers, UI designers prioritize the overall feeling and vibe of a place while also making sure it is useful.
Appearance Vs Feel
UI vs UX design both play important but distinct roles in the creation of a product.
| UI design is concerned with how a product appears, specifically the interactive and visual features that enhance the user experience. | UX design concentrates on the components that will provide users with a relevant and meaningful experience, as well as the general feel of the product or service. |
| UI designers are in charge of designing a layout, creating graphic elements, and making sure the design fits with the branding. | UX designers research, develop prototypes, and do necessary testing to make sure the final product satisfies expectations and goals. |
Design vs. Prototyping
The tasks and objectives of UI vs UX design differ even when they work on the same project.
| UI designers create products and designs that encourage user interaction. | UX designers frequently produce wireframes and functional prototypes that serve as the foundation for a website’s or service’s user flow. |
High-Level vs. Details
The amount of detail that goes into the work of UI and UX designers is an additional difference.
| UI designers work on specific pages, buttons, and user interactions, ensuring that they are well-designed and useful. | UX designers ensure that the overall user flow of a website, service, or app is completely developed and consistent by taking a higher-level viewpoint on the product or service. |
Future of UX/UI Design

The field of product design is always evolving, especially with the influence of AI. Designers must adapt to emerging technologies such as AR and VR, as well as AI-powered personalized services.
The future of design will also depend on the merging of the digital and physical worlds, with a special focus on developing products that focus on user diversity and inclusivity. Designers will need to embrace the new technologies while making sure the products stay user-friendly and intuitive.
Also, a wide range of AI-powered tools and technologies will make the design process more efficient and straightforward. However, low-code and no-code technologies (like Webflow) will keep developing and getting better, but the real question is: Will designers eventually be replaced by them?
We don’t believe that. There are additional reasons for this. Above all, a successful UX design needs to have a “human touch”—that is, an in-depth understanding of human nature and empathy. Because AI is dependent on layouts, it is unable to think creatively or outside the box when it comes to product design.
UX vs UI Designs FAQ’s
Q: How do UX and UI designers collaborate?
For a user-centered product to be successful, UX and UI designers must work together. Several UI and UX designers have discovered that it is easier to work together successfully when there is a common style guide that covers the specifics of a product’s tone, audience, and purpose.
Q: What is the salary for UX and UI designers?
According to Glassdoor, the average salary for UX designers in the United States is $94,260, which includes the basic salary as well as extra compensation such as sales and rewards. UI designers made $98,758 of that amount.
Q: Is learning UX/UI difficult?
Learning UX/UI design can be difficult, but it is dependent on individual talent and dedication. While some people find it easy to use and fun, others might find it difficult at first. Gaining practical experience, learning from reliable sources, and practicing frequently are all necessary to become proficient in UX/UI design.
Conclusion:
In summary, designing a digital product that is both successful and easy to use requires careful consideration of both UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface). UI is centered on the visual and interactive features, whereas UX is more concerned with the complete user journey and satisfaction. Finding an equilibrium between great UX and UI design is essential for creating products that not only meet but also engage and delight users. The cooperation of UI and UX designers is ultimately essential to creating digital experiences that are distinctive and increase user pleasure.
Read Our Article: The Future of Healthcare: Telemedicine App Development 2024

