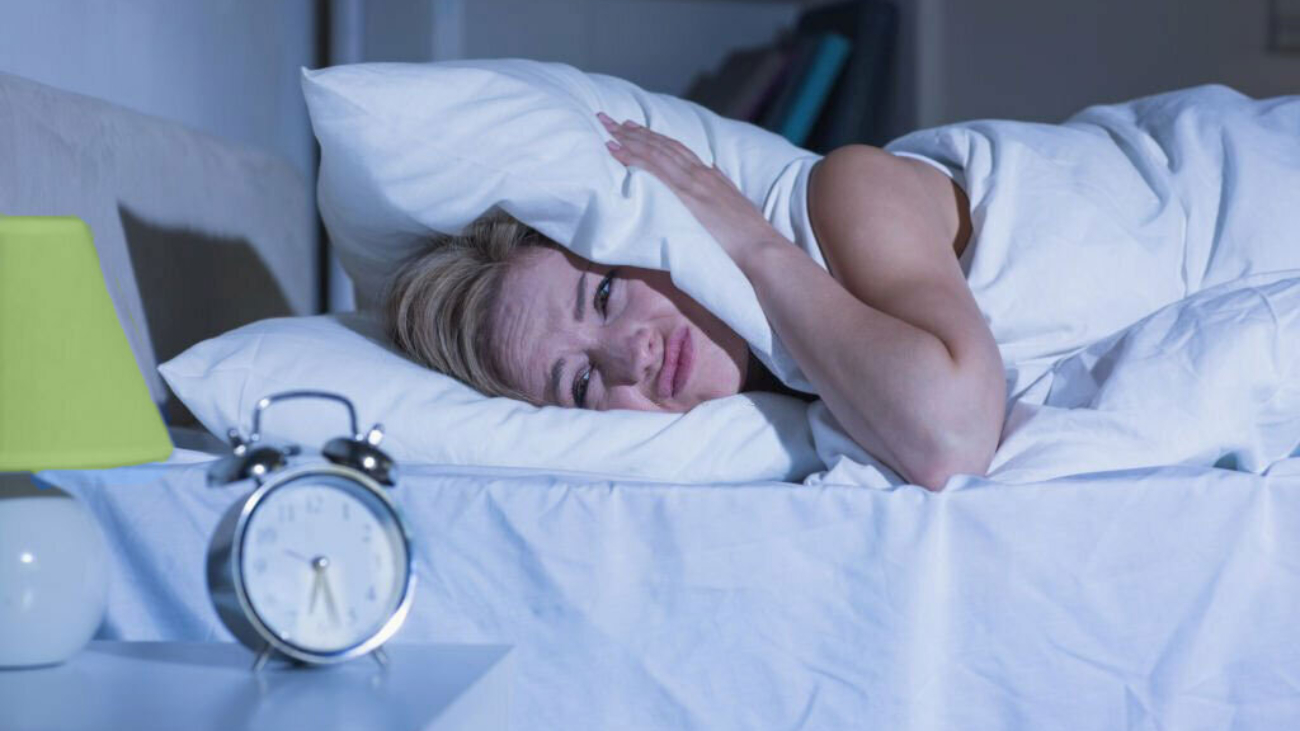
The inability to fall asleep creates worry or stress, which is known as sleep anxiety. Anxiety about how much and how well you will sleep may mess with both the quantity and the quality of your sleep, resulting in a never-ending cycle that causes sleep deprivation and insomnia.
Fortunately, there are methods for dealing with it. Depending on what is causing you sleep anxiety, you may need to change your strategy for reducing it and obtaining the necessary sleep. Treatments that might be beneficial include medication, therapy, and changes in behavior.
What Causes Sleep Anxiety?
Anxiety can cause problems in both nightly life and daily life. Anxiety and sleep deprivation can interact when it comes to sleep difficulties. Depending on what’s causing your sleep anxiety, you may need to adjust your approach to reducing it and obtaining the necessary sleep. First and foremost, it’s important to identify it’s causes. Research has found the following causes for sleep anxiety:
| Adults Affected in U.S. | Percentage of U.S. Adult Population | |
| Generalized Anxiety Disorder | 6.8 million | 3.10% |
| Panic Disorder | 6 million | 2.70% |
| Social Anxiety Disorder | 15 million | 7.10% |
| Specific Phobias | 19.3 million | 9.10% |
| Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder | 2.5 million | 1.20% |
| Post-traumatic Stress Disorder | 7.7 million | 3.60% |
Insomnia
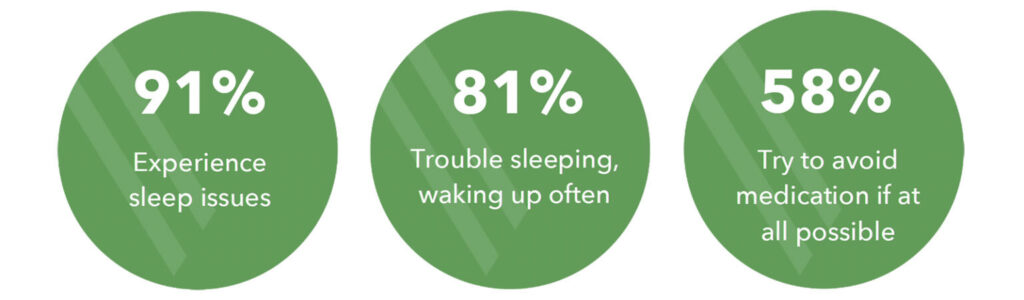
Insomnia is among the most common disorders related to sleep anxiety. In the short term, stress from major life changes such as job changes or relocation may cause insomnia.
- Long-term medical issues or drug side effects could be the cause of insomnia too.
- Insomnia can cause you to stress about how much sleep you’re receiving, which can disrupt your sleep cycle.
- You may notice higher levels of some stress markers, such as the hormone cortisol.
- These higher levels make it harder for you to go to sleep or stay asleep.
- There may be a cyclical link between sleep problems and sleep anxiety.
- Insufficient sleep increases anxiety, which blocks you from getting enough sleep.
Anxiety Disorders
People who suffer from mental health illnesses such as depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) frequently experience difficulties sleeping.
- Sleep deprivation anxiety can develop as a result of getting poor-quality sleep, which may fuel brain functions related to anxiety.
- Some people may be afraid of what sleep may bring, which is why they experience anxiety before bed.
- When trying to suppress painful memories during the day, it troubles you at night to fall asleep.
- People with PTSD may worry about nightmares and flashbacks in their dreams at night.
Symptoms Of Sleep Anxiety:
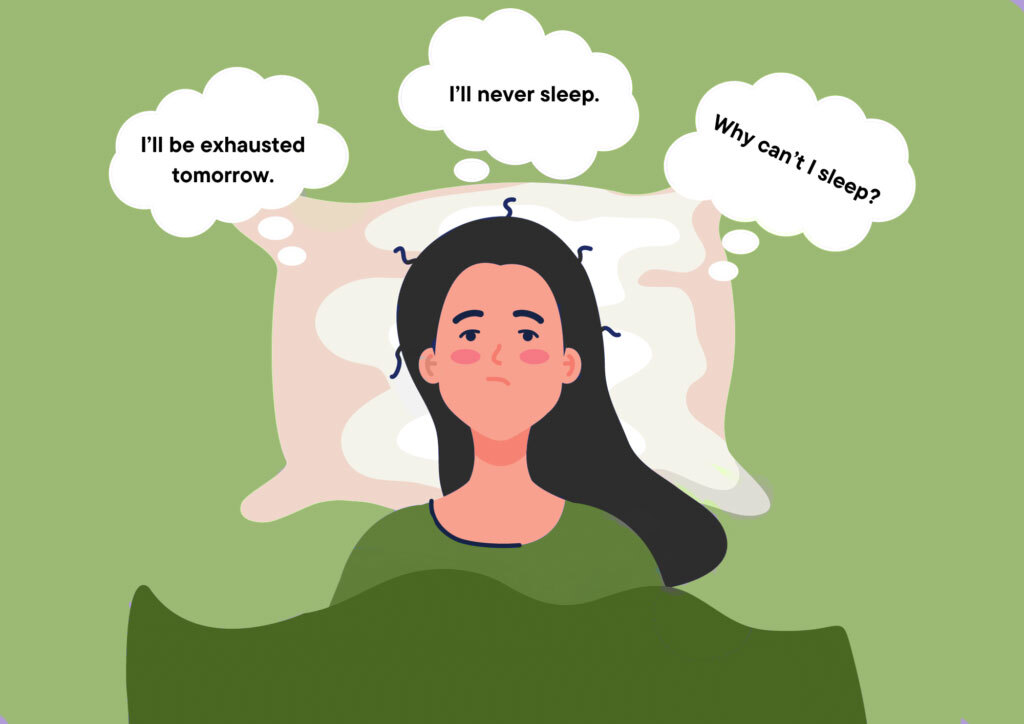

It’s 3 a.m. and you are tired of twisting and turning in your bed, cursing yourself, “Why am I not falling asleep?” which might be due to the following symptoms:
Anxiety-related Insomnia can cause behavioral changes in you, such as:
- Overwhelm-like sensations.
- Unable to focus.
- Intolerance.
- Nervousness.
- Fear of approaching risk or disaster.
You might also be facing some of these physical symptoms.
- Digestive issues.
- High heart rate.
- Fast breathing.
- Sweating.
- Muscle tension.
Also, some people get panic attacks at night. A panic attack is a rapid, powerful, and overwhelming wave of terror that frequently causes you to wake up.
What should I do to overcome Sleep Anxiety?
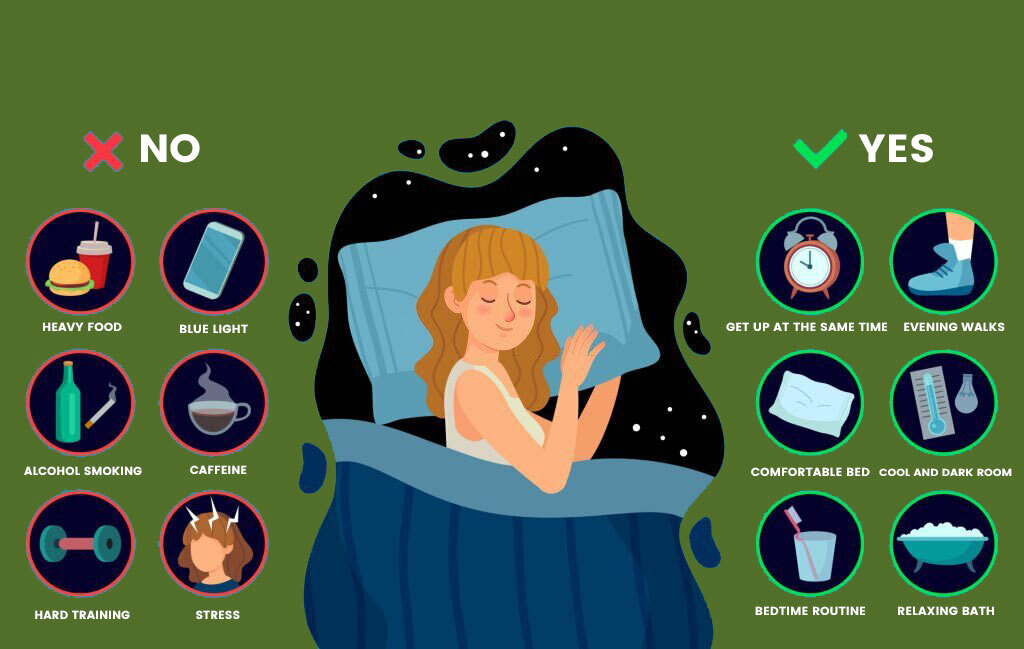
There are many ways to treat sleep anxiety; some of them are given below:
Keeping proper sleeping habits
- Try to go to bed and wake up at a set time.
- Establish a nightly schedule for yourself that includes the same relaxing activities, including listening to soothing music.
- Avoid consuming any type of alcohol or caffeine right before bed.
- Avoid taking naps during the day.
- Don’t go to bed until you’re tired.
- Engage in regular exercise.
- Avoid using sleeping pills on a long-term basis.
- Keep the bedroom dark and cold.
- Sustain a healthy weight.
Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT):
It is a type of therapy that can help people lessen their anxiety about sleeping. It involves meetings with a mental health professional to identify and alter the actions and ways of thinking that cause insomnia.
Treatment with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) may involve behavioral modifications such as maintaining regular sleep schedules, rising from bed at the same time each day, and getting out of bed when anxiety keeps you from sleeping.
Medication:
Sleep anxiety medication can also help reduce fear of sleep.
- The antihistamine ingredient used in some OTC allergy treatments may not be advised for extended periods of time because it can lose its effectiveness with time.
- Additionally, certain prescription drugs have the potential to become habits, so you and your doctor will need to closely monitor how the medicine affects you while you’re receiving therapy.
- Inquire about melatonin pills from your healthcare physician as well. Although some people have found them to be a helpful sleep aid, further research is required to determine their long-term safety.
Conclusions:
Sleep anxiety is a serious condition that can have significant impacts on your life. Even though it’s not the same as generalized anxiety, if it gets severe, you should speak with a doctor or certified therapist about options for therapy. Remember that it could take some time to resume regular sleep patterns when you start to feel anxious. Appreciate the little things in life, concentrate on creating healthy sleeping habits, and return to practical relaxing methods when you’re having issues.
Read our article What Are The Best SEO Strategies For Your Website?

